Geostationary Satellite Orbits At An Elevation Of
A geostationary satellite is a type of geosynchronous satellite.
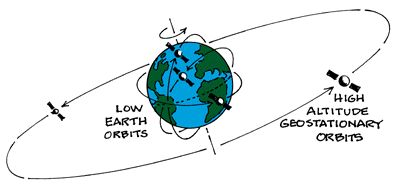
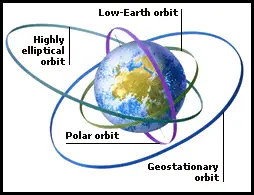
Geostationary satellite orbits at an elevation of. Satellites in low inclination orbits can get an energy boost from the earth s rotation by being launched near the equator. 5 india s geosynchronous satellite launch vehicle pulled off a similar feat with the gsat 14 communications satellite. Thus a geostationary orbit is defined as a geosynchronous orbit at zero inclination. Geostationary orbits fall in the same category as geosynchronous orbits but it s parked over the equator.
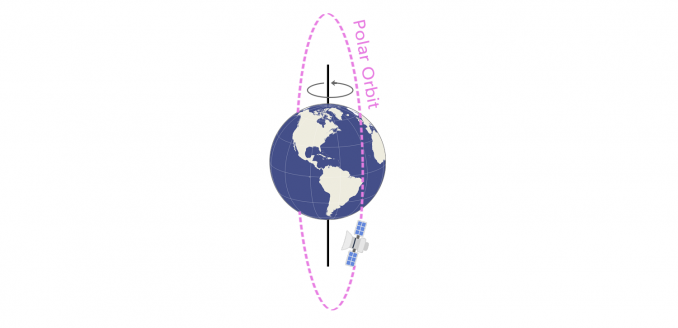
Since earth also rotates once in 24 hours a satellite at 22 223 miles altitude stays in a fixed position relative to a point on earth s surface. This one special quality makes it unique from geosynchronous orbits. Looking at the definitions of both geostationary and geosynchronous orbits outlined above it s quite clear that there is very little difference between the two. On the other hand high inclination satellites don t receive much benefit from equatorial launch sites.
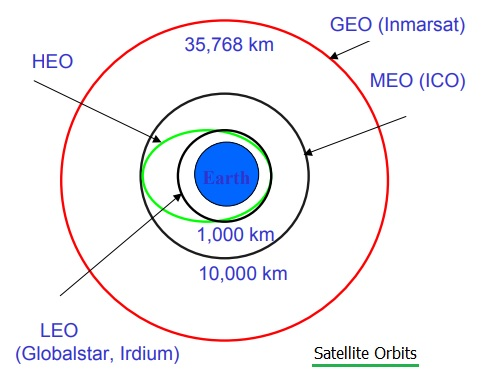
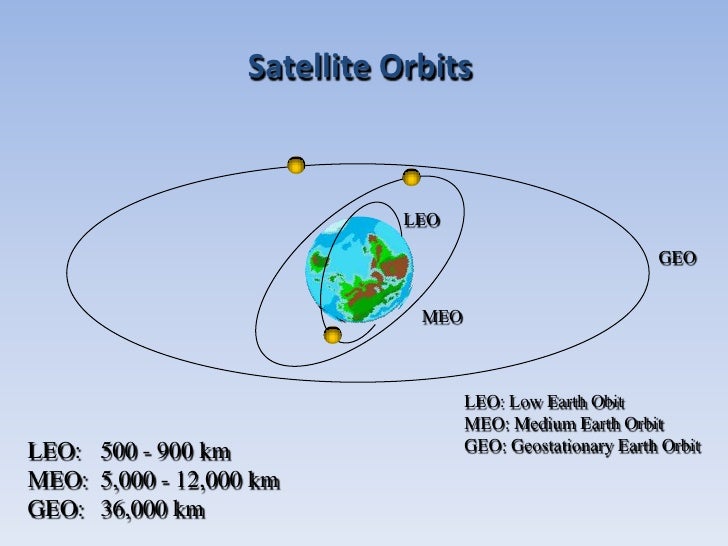
Both complete one full orbit of earth per sidereal day relative to the stars not the sun. I ve been writing a lot about geostationary satellites lately. The elevation angles used in the above maps have been calculated assuming a straight line between you and the satellite. Geosynchronous and geostationary orbits have a semi major axis of 42 164 km 26 199 mi.
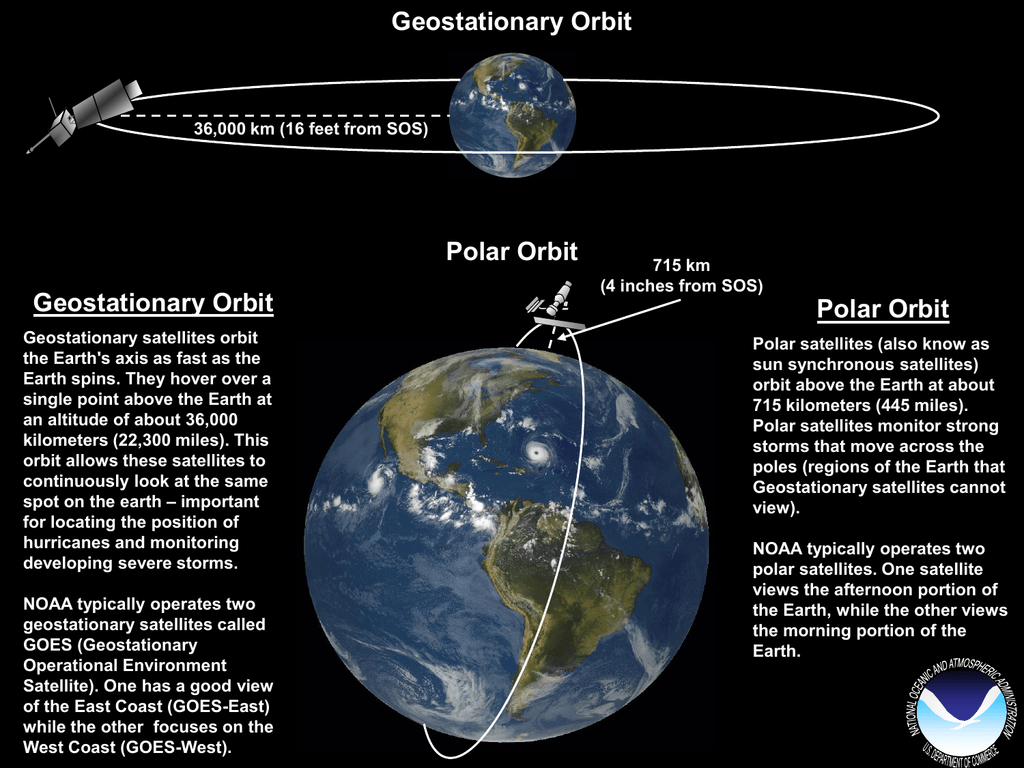
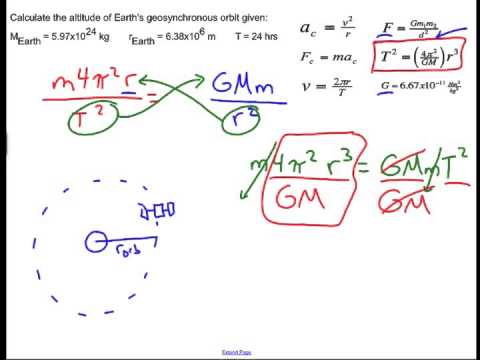
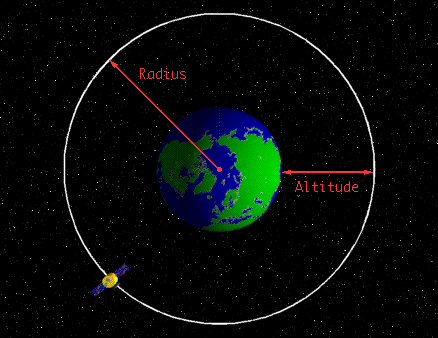
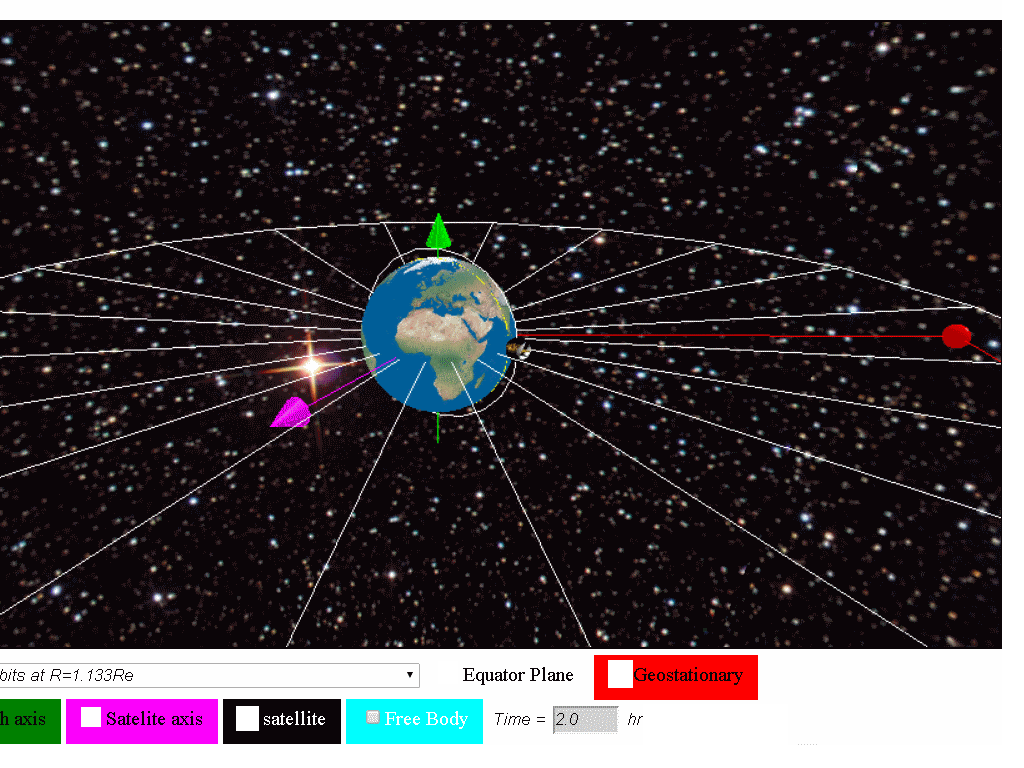
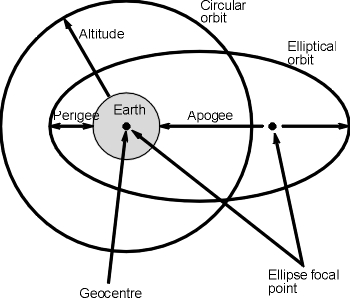
A geostationary orbit also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35 786 kilometres 22 236 miles above earth s equator and following the direction of earth s rotation. This works out to an altitude of 35 786 km 22 236 mi. As i wrote about the gslv d5 mission i was tempted to include this. In december spacex s upgraded falcon 9 rocket placed the ses 8 communications satellite into geostationary transfer orbit and on jan.
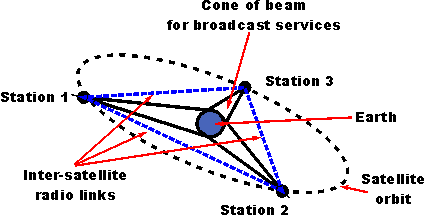
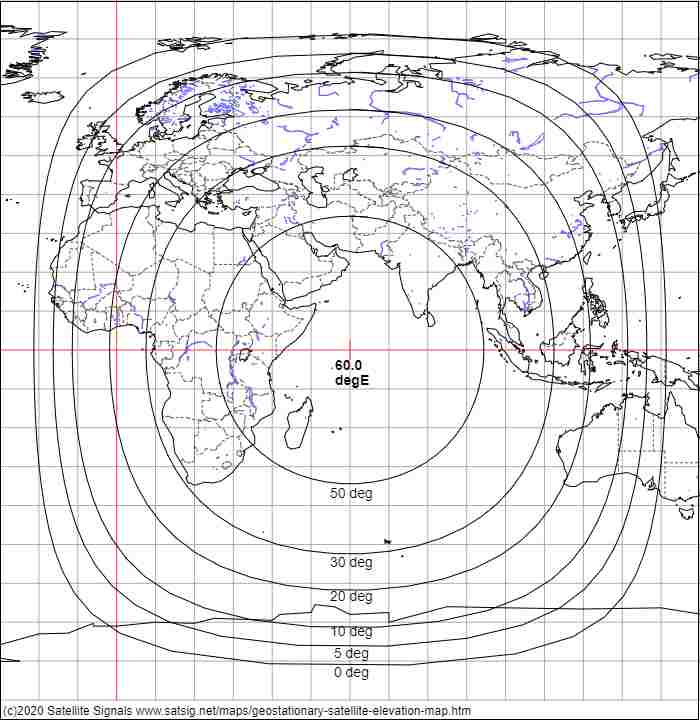
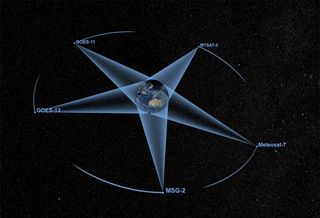
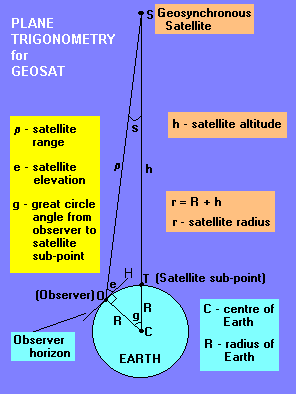
The european space agency launches satellites into geostationary orbits from their facilities in french guiana left. Enter your latitude and longitude and our geostationary satellite calculator will compute the satellite elevation azimuth and range from each satellite to your position. Weather monitoring satellites like goes are in geostationary orbits because they have a constant view of the same area. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to the earth s rotational period one sidereal day and so to ground observers it appears motionless in a fixed.
A geosynchronous orbit sometimes abbreviated gso is an earth centered orbit with an orbital period that matches earth s rotation on its axis 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds one sidereal day the synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that for an observer on earth s surface an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period.